Treatment
Treatment for OSA is typically related to the severity of the condition and the associated co-morbidities (additional existing chronic conditions).
Conservative Measures
For milder cases of obstructive sleep apnea, your doctor may recommend conservative measures or lifestyle changes such as:
- Lose weight if you're overweight
- Exercise regularly
- Drink alcohol moderately, if at all, and don't drink several hours before bedtime
- Quit Smoking
- Use a nasal decongestant or allergy medications
- Avoid sleeping on your back
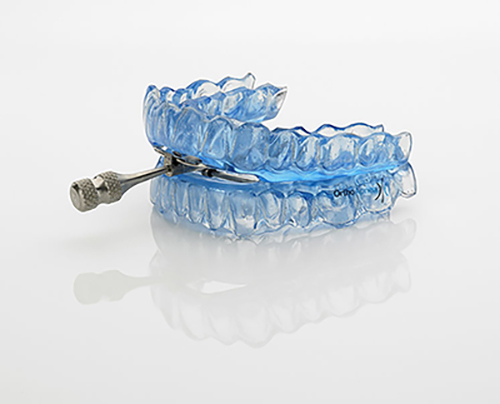

Oral Appliance
An oral appliance is a device that repositions the lower jaw forward during the sleep and this in turn, helps maintain the airways open. An oral device could help with snoring and mild cases but is not usually effective for moderate or severe cases.
Oral Surgery
In mild to moderate cases oral surgery may be considered. This is a less common option since is more invasive and it does not have a lasting, reliable effect.
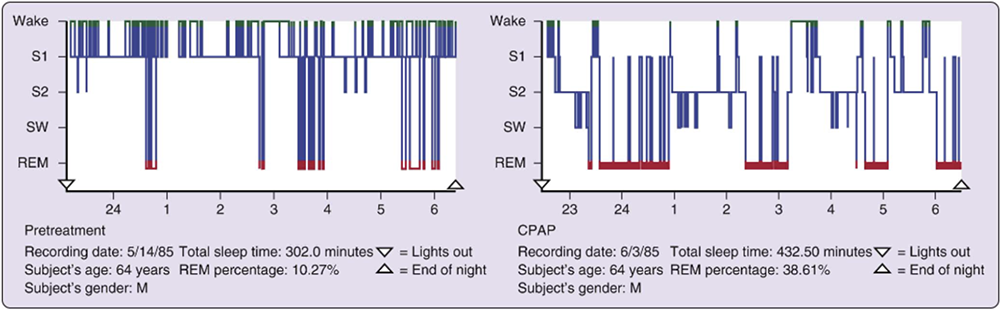
Positive Airway Pressure therapy (PAP)is the most effective treatment for OSA

Positive airway pressure has a variety of modes with the most common ones being the Continuous (constant) PAP and Automatic (auto-adjusting) PAP.
This form of treatment uses a machine that delivers air pressure to achieve a pneumatic splint and maintain your airways open.
An interface (mask) seals over the nostrils, the nose, or both the nose and mouth for efficient therapy.
Sleep histogram comparing sleep quality before and after treatment with CPAP therapy.